View Tables in Different Modes¶
Contents
To efficiently inspect table data, it is very useful to change table view modes.
Dual View¶
In dual view mode, table is split into two part and each part can be scrolled and zoomed independently. This mode is useful to inspect large data.
Dual view is enabled by setting table.view_mode = "horizontal" for horizontal
view, and table.view_mode = "vertical" for vertical one.
table = viewer.add_table(data)
table.view_mode = "horizontal"
To reset dual view, set the property to "normal".
table.view_mode = "normal"
Dual view can also be turned on by key combo Ctrl K ⇒ H (horizontal) or Ctrl K ⇒ V (vertical). Reset it by key combo Ctrl K ⇒ N.
Popup View¶
In popup view mode, a large popup window appears and the table data is shown inside it. This mode is useful when you want to focus on seeing or editing one table, or the table viewer widget is docked in other widget so it is very small.
Popup view is enabled by setting table.view_mode = "popup" and can be reset
similar to dual view by table.view_mode = "normal"
table = viewer.add_table(data)
table.view_mode = "popup"
Dual view can also be turned on by key combo Ctrl K ⇒ P.
Tile View¶
Tile view is a mode that shows different tables in a same window, while the structure of table list and tabs are not affected.
How tiling works¶
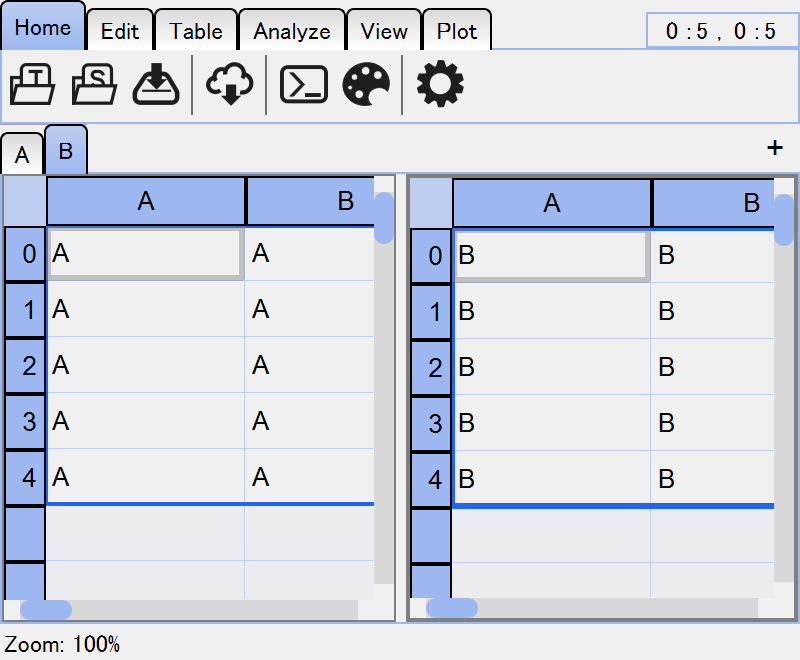
For instance, if you tiled tables “A” and “B”, they will appear in the same
window, but tabs named “A” and “B” still exist in the tab bar. viewer.tables[i]
also returns the same table as before. When tab “A” or “B” is clicked, the tiled
table with “A” and “B” is shown as A|B.
You can tile the current table and the table next to it by shortcut Ctrl K ⇒ ^.
You can also programmatically tile tables by calling viewer.tables.tile().
viewer.tables.tile([0, 1]) # tile the 0th and 1st tables
viewer.tables.tile([0, 1, 3]) # tile tables at indices [0, 1, 3]
Untiling¶
Untiling is also well-defined operation. Let’s say tabs “A”, “B” and “C” is tiled so
these tabs show tiled view A|B|C. If you untiled “B”, “A” and “C” are re-tiled
while “B” returns the original state. Therefore, tabs “A” and “C” shows A|C and
tab “B” shows B.
You can untile the current table by shortcut Ctrl K ⇒ \.
You can also programmatically untile tables by calling viewer.tables.untile([0, 1, 2]).